
A Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) is a file that functions like a real physical hard drive. It allows you to store data, install operating systems, or test software without altering your existing system setup. VHDs are especially useful for developers, IT administrators, and power users who need a secure, isolated, and easily manageable environment to work in.
In Windows 11, creating and managing a VHD is straightforward thanks to built-in tools like Disk Management and PowerShell. Once created, you can mount it just like any other drive and use it for backups, virtual machines, or experimental projects.
What Is a Virtual Hard Disk (VHD)?
A Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) is essentially a single file that emulates a physical hard drive. It can store data, folders, system files, or even complete installations of operating systems. The VHD file has an extension like .vhd or .vhdx, depending on the format.
Here’s what each format means:
- VHD (.vhd): The original format compatible with older versions of Windows (like Windows 7 and earlier). It supports a maximum file size of 2 TB.
- VHDX (.vhdx): The newer, more advanced format introduced with Windows 8 and later. It supports up to 64 TB and offers better performance and reliability.
The VHDX format is preferred in Windows 11 because it provides resilience against corruption and supports larger virtual disks.
Why Create a Virtual Hard Disk?
Before jumping into the steps, let’s look at why users often create VHDs in Windows 11:
- Data Isolation: Keep sensitive files separate from your main partitions.
- Safe Testing Environment: You can install another operating system or software inside a VHD without affecting your primary setup.
- File Organization: Use it as a separate drive to store data, backups, or archives.
- System Backup: Create full system backups in a VHD format for easy recovery later.
- Portability: A VHD file can be easily copied or transferred to other systems or virtual machines.
- Virtualization: You can attach VHDs in virtualization platforms like Hyper-V or VirtualBox to run multiple OS environments.
Types of Virtual Hard Disks
VHD files come in three primary types, each optimized for different use cases.
Fixed-size VHDs allocate their full specified capacity immediately upon creation, resulting in files that match their configured disk size. While this approach consumes more storage space initially, it offers better performance since no dynamic allocation occurs during operation.
Dynamic VHDs start small and grow as data is added, expanding up to their maximum configured size. This approach conserves storage space by only allocating what’s actually needed, making them ideal for scenarios where disk space efficiency is crucial. However, this flexibility can result in slightly reduced performance due to the overhead of dynamic expansion.
Differencing VHDs represent a third category, functioning as child disks that store only changes made to a parent VHD. This creates a chain relationship where multiple virtual machines can share a common base image while maintaining individual modifications. This approach is particularly valuable for deployment scenarios where multiple similar systems need to be created efficiently.
How to Enable VHD in Windows 11: Using Disk Management (Built-in Tool)
Step 1: Open Disk Management
Press Windows key + X and select “Disk Management.”
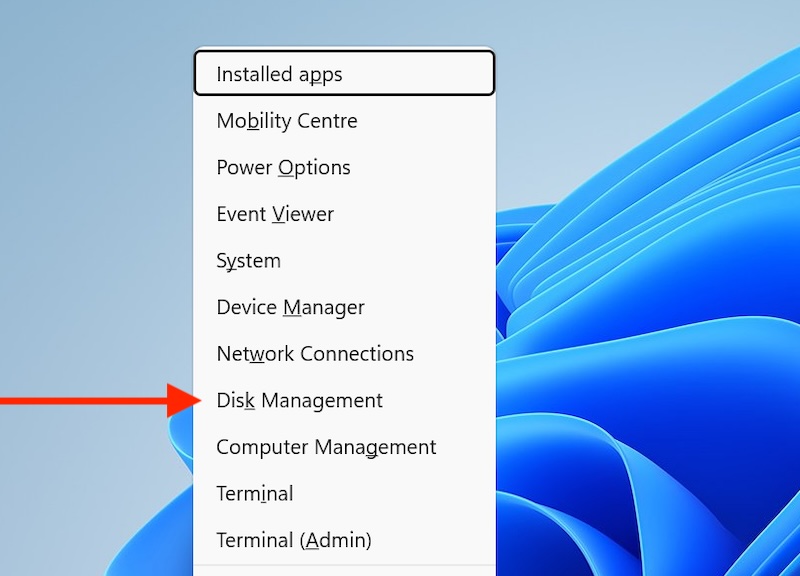
Or search for “Disk Management” in the Start menu and run it as Administrator.
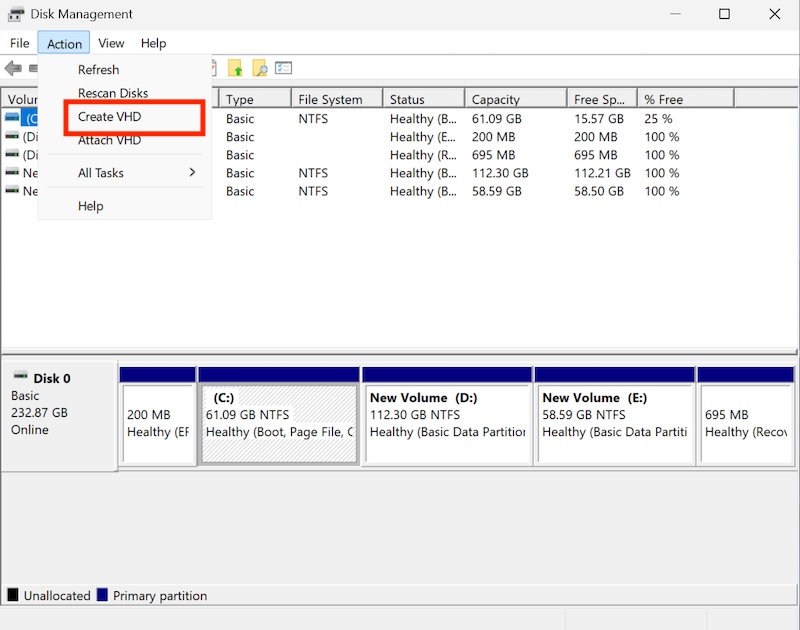
Step 2: Create a VHD
In Disk Management, click on the “Action” menu.
Select “Create VHD.”
Choose location and filename for your VHD file.
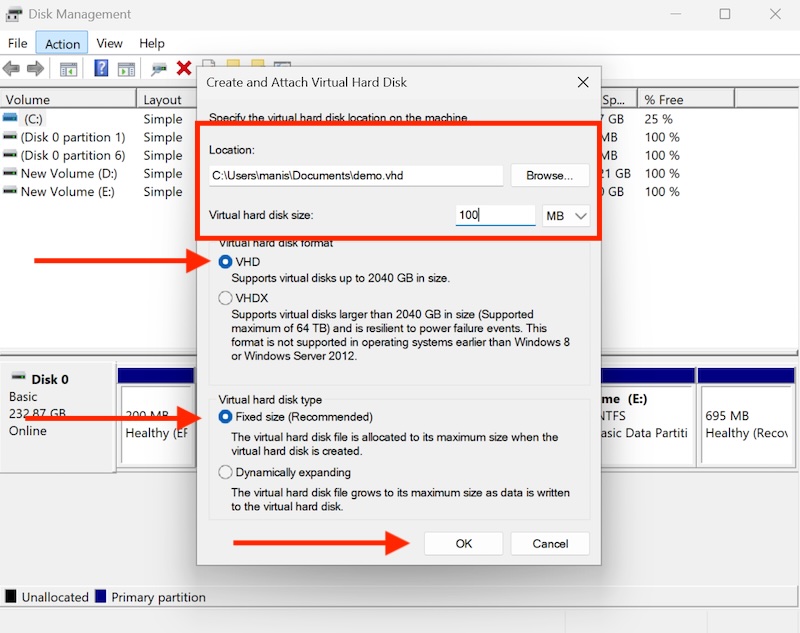
Set the virtual hard disk size.
Select format type (VHD or VHDX) and choose between “Fixed size” or “Dynamically expanding.”
Step 3: Attach/Mount a VHD
From Disk Management, expand the Action menu and select “Attach VHD.”
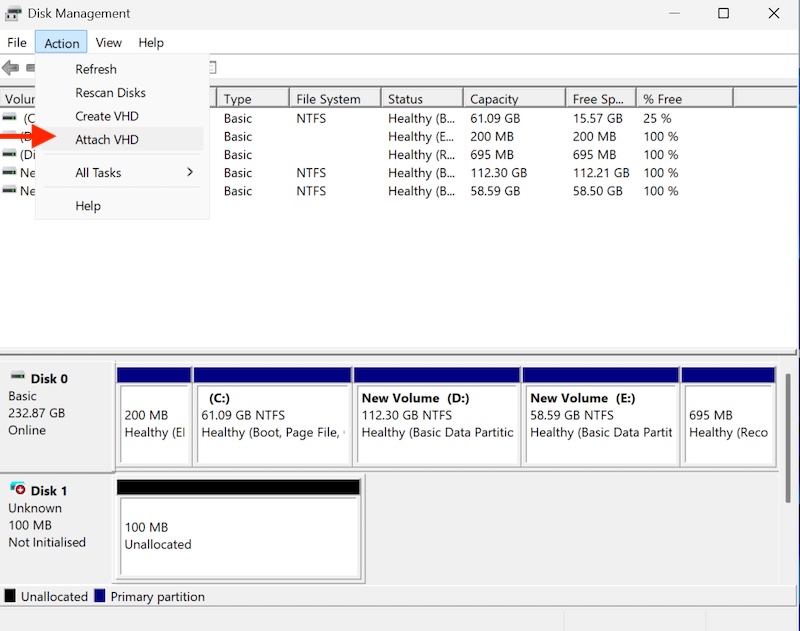
Browse to locate your VHD/VHDX file.
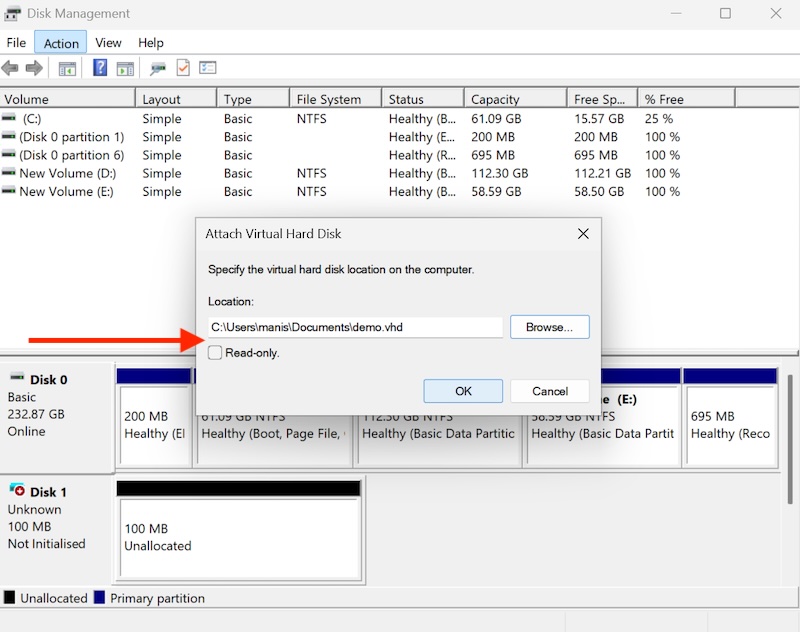
Click “OK” to attach it
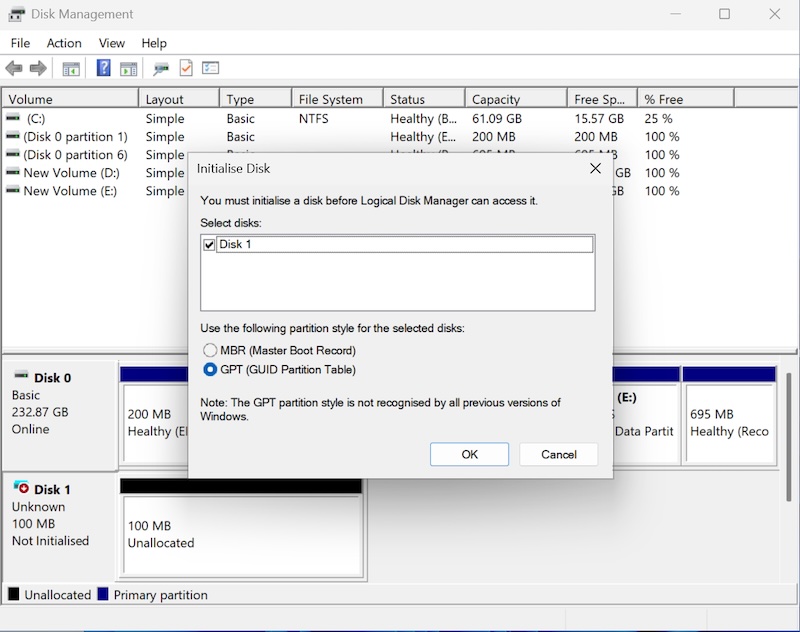
Step 4: Initialize the VHD
Select GPT or MBR for the Partition Style and click Initialize.
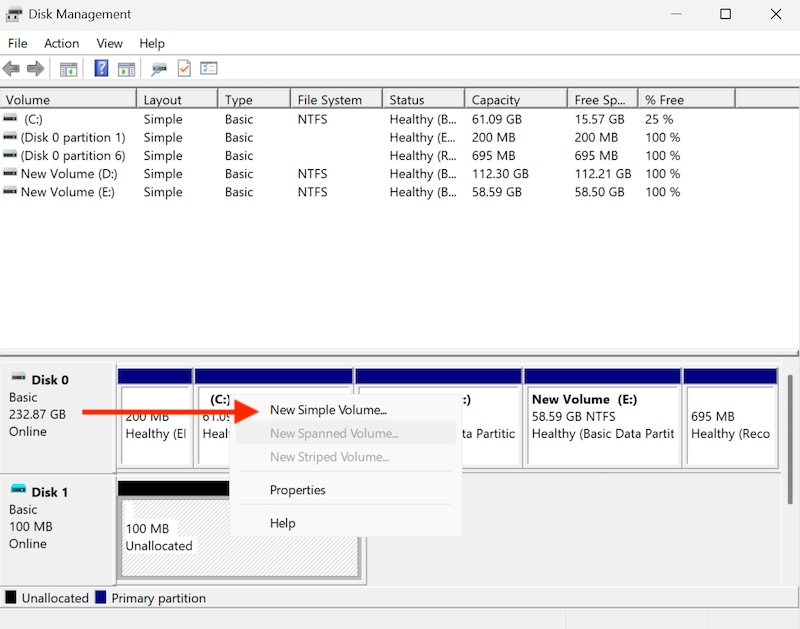
Right-click the unallocated space and select “New Simple Volume.”
Follow the wizard to format and assign a drive letter.
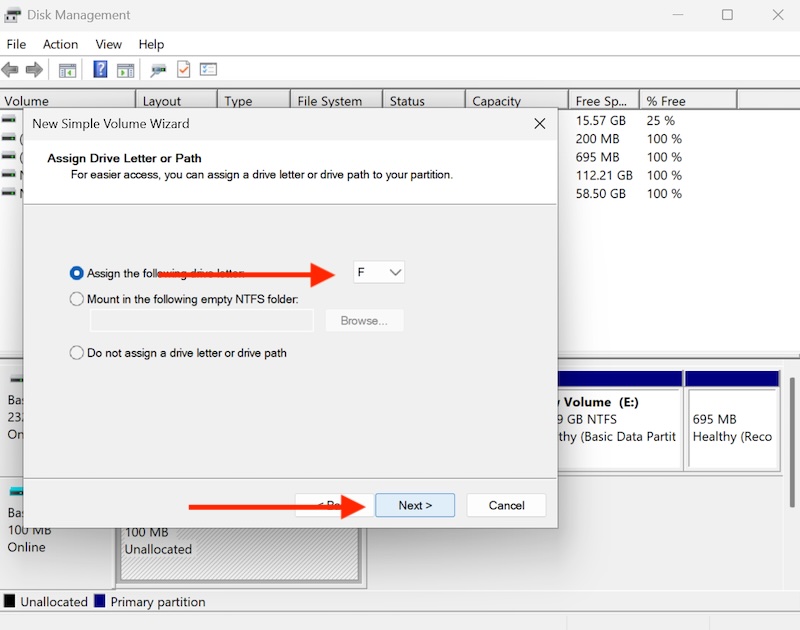
Click on Next.
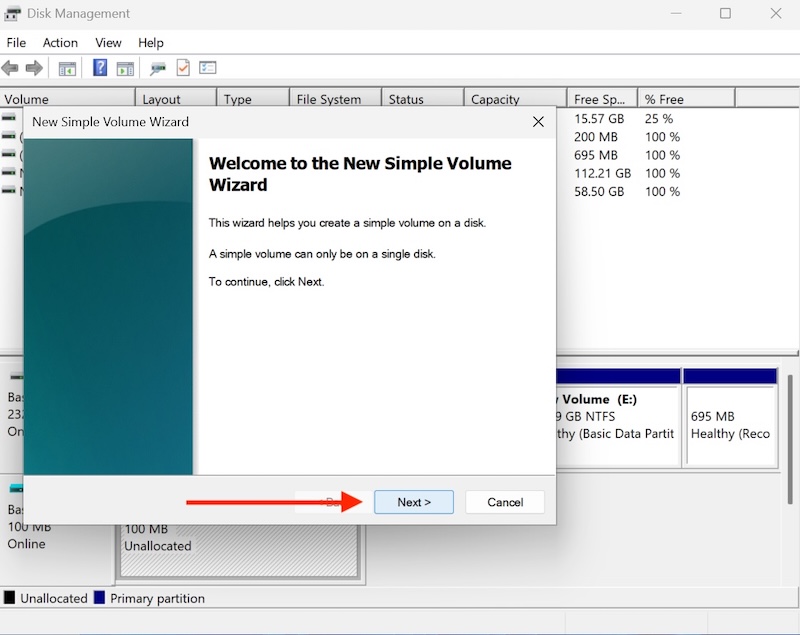
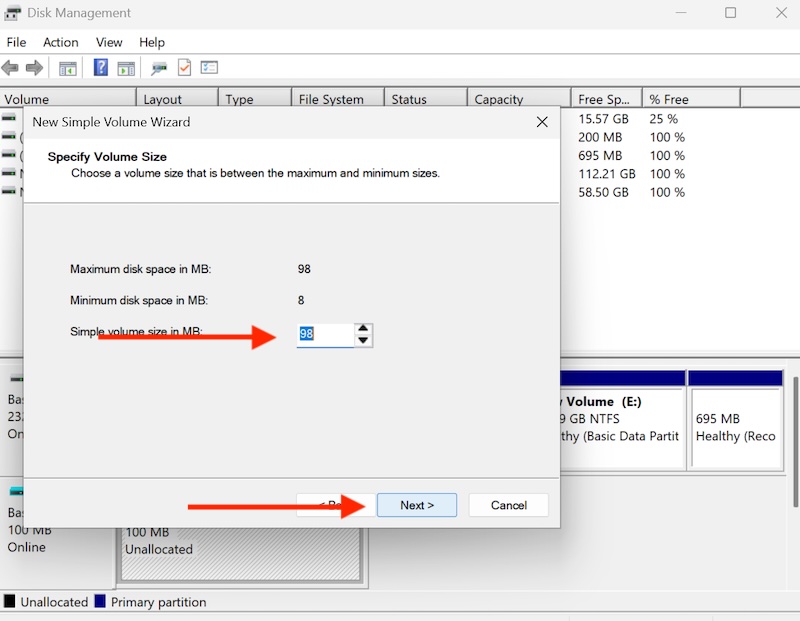
Select Volume Size Equal or Less Than the size selected for your VHD.
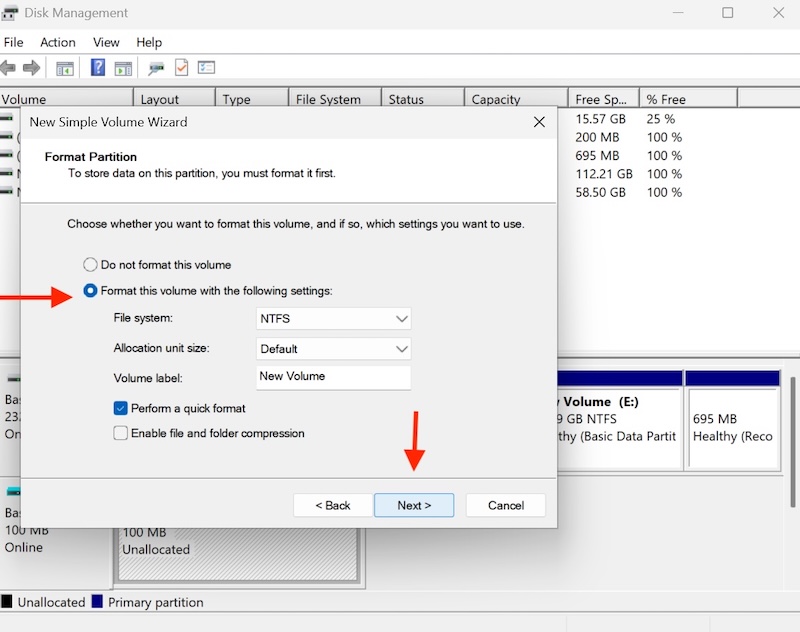
Select the volume format options and click Next.
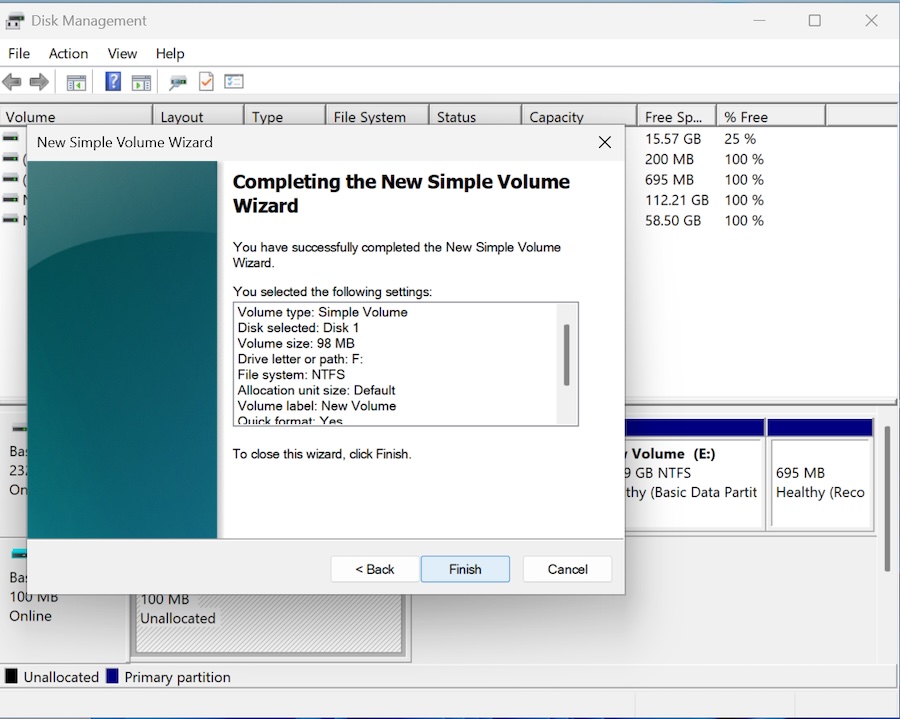
Finally, you are done and click on Finish to complete the process.
Practical Applications
Virtual hard disks serve numerous practical purposes across various computing environments. In virtualization platforms like Hyper-V, VMware, and VirtualBox, VHDs house complete operating system installations, allowing multiple virtual machines to run simultaneously on a single physical host. This capability enables server consolidation, testing environments, and development platforms without requiring dedicated hardware for each system.
Cloud computing services extensively utilize VHD technology to provide scalable storage solutions. Virtual machines in cloud environments typically boot from VHD files, enabling rapid deployment and migration of workloads across different physical servers. The portability of VHD files makes it possible to move entire systems between data centers or cloud providers with relative ease.
System backup and disaster recovery represent another significant application area. Organizations can create complete system images as VHD files, capturing not just data but entire operating environments. These images can be quickly restored to virtual machines or even different physical hardware, providing robust recovery options that minimize downtime during system failures.
Advantages of Using VHD
The VHD format offers several compelling advantages over traditional storage approaches.
1. Portability and Mobility
VHD files offer unparalleled portability, allowing entire operating systems and applications to be moved between different physical machines, hypervisors, or cloud platforms with minimal effort. This mobility eliminates the traditional constraints of hardware-specific installations, enabling seamless migration of virtual environments across diverse computing infrastructures. Organizations can easily relocate workloads for load balancing, disaster recovery, or infrastructure upgrades without complex reinstallation procedures.
2. Storage Efficiency and Space Optimization
Dynamic VHDs provide significant storage savings by allocating space only as needed, rather than reserving the full configured capacity upfront. This approach can reduce storage requirements by 60-80% in typical deployment scenarios. Differencing VHDs further enhance efficiency by allowing multiple virtual machines to share common base images while maintaining individual customizations, dramatically reducing storage footprint for standardized deployments.
3. Simplified Backup and Recovery
VHD technology streamlines backup operations by encapsulating entire systems within single files that can be easily copied, archived, or replicated. This approach enables point-in-time system snapshots, rapid bare-metal recovery, and simplified disaster recovery procedures. Organizations can restore complete environments to different hardware platforms or virtual infrastructures without complex migration processes.
4. Enhanced Development and Testing
VHD files facilitate agile development workflows by providing isolated, reproducible environments that can be quickly created, modified, or discarded. Developers can maintain multiple system configurations, test different software versions, or experiment with various configurations without affecting production systems. The ability to revert to previous states through snapshots accelerates troubleshooting and reduces development cycle times.
5. Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
By consolidating multiple virtual machines on single physical hosts, VHD technology reduces hardware acquisition costs, power consumption, and data center space requirements. Organizations can achieve higher server utilization rates while maintaining operational flexibility. The reduced need for physical storage hardware and simplified management procedures further contribute to operational cost savings.
6. Scalability and Flexibility
VHD technology supports rapid scaling of computing resources to meet changing business demands. New virtual machines can be deployed within minutes using template-based approaches, while differencing disks enable efficient creation of multiple similar systems. This scalability supports both planned capacity expansion and sudden workload spikes without significant infrastructure investments.
Technical Considerations and Limitations
While VHD technology offers numerous benefits, certain limitations must be considered. The original VHD format has a maximum size limit of 2 terabytes, which can be restrictive for modern large-scale applications. The newer VHDX format addresses this limitation, supporting virtual disks up to 64 terabytes.
Performance considerations also merit attention, as VHD files add a layer of abstraction between the virtual machine and physical storage. While modern implementations minimize this overhead, applications with intensive disk I/O requirements may experience measurable performance differences compared to direct physical disk access.
Fragmentation can become an issue with dynamic VHDs, as frequent expansion and contraction may result in scattered data blocks across the host file system. Regular maintenance, including compaction operations, may be necessary to maintain optimal performance.
Future Developments
Virtual hard disk technology continues evolving alongside broader trends in virtualization and cloud computing. Enhanced security features, including encryption capabilities, are being integrated to protect sensitive data within VHD files. Improved compression algorithms are reducing storage requirements while maintaining performance levels.
Integration with modern storage technologies, such as solid-state drives and NVMe interfaces, is optimizing VHD performance for contemporary hardware platforms. Additionally, cloud-native enhancements are improving the efficiency of VHD operations in distributed computing environments.
Virtual hard disks have become fundamental components of modern computing infrastructure, enabling flexible, efficient, and portable storage solutions that support the dynamic requirements of virtualized environments. Their continued development ensures they will remain relevant as computing architectures continue evolving toward increasingly virtualized and cloud-centric models.
Conclusion
Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) technology has revolutionized storage management by encapsulating entire disk systems within portable files. From its Connectix origins to seamless Windows 11 integration, VHD has become essential for modern computing infrastructure. The three VHD types—fixed-size, dynamic, and differencing—provide versatile solutions for diverse scenarios, from high-performance production environments to space-efficient development workflows.
Windows 11’s native VHD support through Disk Management, Settings, and command-line tools demonstrates the technology’s maturity and accessibility. Users can effortlessly create, mount, and manage virtual disks without third-party software, making VHD functionality available across all skill levels.
The practical advantages of portability, storage efficiency, simplified backup and recovery, and streamlined deployment have made VHD indispensable for virtualization strategies, cloud computing, and disaster recovery. As computing environments become increasingly virtualized and distributed, VHD technology continues evolving with enhanced security features and performance optimizations, ensuring its continued relevance in tomorrow’s digital landscape.








