
Keeping your drivers up to date is crucial for optimal system performance, hardware compatibility, and security in Windows 11. Drivers act as translators between your operating system and hardware components, ensuring everything works smoothly together. This comprehensive guide will walk you through multiple methods to update your drivers, from automatic Windows updates to manual installations.
Why Update Drivers?
Keeping your device drivers updated is one of the most important maintenance tasks for any Windows 11 system. Understanding the reasons behind driver updates helps you make informed decisions about system maintenance and troubleshooting.
Enhanced System Performance
Updated drivers are specifically optimized to work with the latest version of Windows 11 and can significantly improve your system’s overall performance. Manufacturers continuously refine their driver code to reduce CPU usage, minimize memory consumption, and optimize resource allocation. Graphics drivers, for example, often include performance improvements that can boost gaming frame rates by 10-15% or more. Network drivers receive updates that enhance connection stability and data transfer speeds, while storage drivers can improve read and write operations for faster file access.
Bug Fixes and Stability Improvements
Driver updates frequently address known issues that cause system crashes, hardware malfunctions, or unexpected behavior. These bugs might manifest as blue screen errors, device disconnections, audio crackling, or display glitches. Manufacturers identify these problems through user feedback, internal testing, and compatibility assessments with new software releases. Updated drivers eliminate these issues, resulting in a more stable and reliable computing experience.
Security Enhancements
Outdated drivers can create security vulnerabilities that malicious software can exploit to gain unauthorized access to your system. Driver updates often include critical security patches that close these loopholes and protect your computer from emerging threats. This is particularly important for network adapters, USB controllers, and graphics drivers, which interact directly with external devices and internet connections.
Hardware Compatibility
As Windows 11 receives regular updates and new software is released, compatibility requirements change. Updated drivers ensure your hardware remains fully compatible with the latest operating system features and third-party applications. Without current drivers, you might experience reduced functionality, missing features, or complete hardware failure when using newer software.
Access to New Features
Many driver updates introduce new capabilities and features that weren’t available in previous versions. Graphics drivers might add support for new gaming technologies like ray tracing or DLSS, while audio drivers could include enhanced sound processing algorithms or support for new audio formats. These updates essentially expand your hardware’s capabilities without requiring physical upgrades.
Manufacturer Support
Using outdated drivers may void your hardware warranty or limit your eligibility for technical support from manufacturers. Keeping drivers current ensures you can access full manufacturer support when needed and demonstrates that you’re maintaining your system according to recommended guidelines.
Regular driver updates are essential for maintaining optimal system performance, security, and functionality in Windows 11.
Method 1: Using Windows Update (Recommended for Most Users)
Windows 11 automatically searches for and installs many driver updates through Windows Update. This is the safest and most convenient method for most users.
Step 1: Access Windows Update Press the Windows key + I to open Settings, or right-click the Start button and select “Settings.” In the Settings window, click on “Windows Update” in the left sidebar. You’ll see the Windows Update panel with options to check for updates.

Step 2: Check for Updates Click the “Check for updates” button. Windows will search for available updates, including driver updates. This process may take several minutes depending on your internet connection and the number of available updates. Windows will display a list of available updates, including system updates and driver updates.
Step 3: Install Driver Updates If driver updates are found, they’ll be listed separately or included in the general update list. Click “Download & install” to begin the installation process. Some updates may require a restart, which Windows will prompt you about. Allow the system to restart if required, and the driver installation will complete automatically.
Step 4: Verify Installation After the restart, return to Windows Update to ensure all updates were installed successfully. You can also check the “Update history” to see which drivers were updated.
Method 2: Using Device Manager
Device Manager provides more granular control over individual device drivers and is useful when you need to update specific hardware components.
Step 1: Open Device Manager Right-click the Start button and select “Device Manager” from the context menu. Alternatively, press Windows key + X and select “Device Manager,” or type “Device Manager” in the Start menu search and click the result.
Step 2: Locate the Device Device Manager displays all your hardware components organized by category. Expand the relevant category to find the device whose driver you want to update. Devices with driver issues often display a yellow warning triangle or red X icon.
Step 3: Update the Driver Right-click on the specific device and select “Update driver” from the context menu. A new window will appear with two options: “Search automatically for drivers” and “Browse my computer for drivers.”

Step 4: Choose Update Method Select “Search automatically for drivers” to let Windows search for the best available driver online. This method is recommended for most users as it’s safer and more reliable. Windows will search its database and the internet for compatible drivers and install the best match automatically.
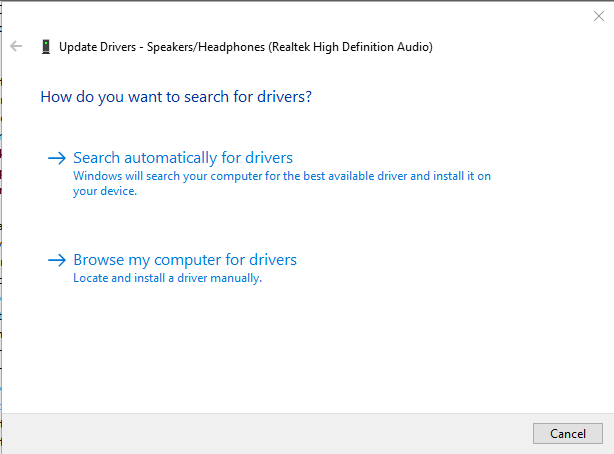
Step 5: Complete the Installation Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the driver installation. If Windows finds a newer driver, it will download and install it automatically. You may need to restart your computer to complete the installation process.
Method 3: Downloading from Manufacturer Websites
For the most current drivers and specialized features, downloading directly from hardware manufacturers’ websites is often the best approach.
Step 1: Identify Your Hardware Before visiting manufacturer websites, you need to identify your specific hardware. In Settings, click on the”System.” Go to the “about” tab to check your computer specs. Note down the hardware information, or alternatively, use system information tools like “msinfo32” to gather comprehensive hardware details.

Step 2: Visit Manufacturer Websites Go to your hardware manufacturer’s official website. Major manufacturers include NVIDIA and AMD for graphics cards, Intel and AMD for processors, and specific manufacturers like Dell, HP, or Lenovo for laptops and pre-built computers.
Step 3: Navigate to Support Section Look for a “Support,” “Downloads,” or “Drivers” section on the manufacturer’s website. These are usually located in the main navigation menu or footer of the website.
Step 4: Find Your Product Use the search function or browse categories to find your specific product model. Many manufacturers offer automatic detection tools that can scan your system and recommend appropriate drivers.
Step 5: Download and Install Download the latest driver package for your operating system (Windows 11). Ensure you’re downloading the correct version for your system architecture (32-bit or 64-bit). Run the downloaded installer as an administrator by right-clicking and selecting “Run as administrator.” Follow the installation wizard prompts, and restart your computer when prompted.
Method 4: Using Third-Party Driver Update Software
While not always necessary, third-party driver update tools can be helpful for comprehensive system scans and bulk driver updates.
Popular and Reputable Options Some well-known third-party driver update tools include Driver Booster, Driver Easy, and Snappy Driver Installer. However, exercise caution when choosing third-party software, as some programs may install unwanted software or incorrect drivers.
Step 1: Research and Download Research the tool thoroughly, reading reviews and checking for certifications. Download only from official websites to avoid malware. Install the software following standard installation procedures.
Step 2: Scan Your System Launch the driver update software and initiate a system scan. The software will analyze your hardware and compare installed drivers with available updates from its database.
Step 3: Review and Install Updates Review the scan results carefully. Most reputable software will show you which drivers are outdated and provide details about the updates. Select the drivers you want to update and proceed with the installation. Create a system restore point before installing multiple drivers at once.
Method 5: Windows Update Catalog (Advanced Users)
The Windows Update Catalog is Microsoft’s repository of updates and drivers, useful for downloading specific updates manually.
Step 1: Access the Catalog Open your web browser and navigate to the Microsoft Update Catalog website. This is an official Microsoft resource containing all available updates and drivers.
Step 2: Search for Drivers Use the search function to find specific drivers by entering hardware names, model numbers, or update KB numbers. You can filter results by product, classification, and other criteria.
Step 3: Download and Install Find the appropriate driver for your system and click “Download.” Extract the downloaded files if necessary and install the driver manually through Device Manager by selecting “Browse my computer for drivers” and pointing to the downloaded files.
Best Practices and Tips
Create System Restore Points Before installing any drivers, especially multiple ones, create a system restore point. This allows you to rollback changes if something goes wrong. Type “Create a restore point” in the Start menu and follow the prompts.
Install One Driver at a Time When updating multiple drivers, install them one at a time and restart between installations when required. This makes troubleshooting easier if issues arise.
Keep Driver Installation Files Save downloaded driver files in a dedicated folder for future reference. This is particularly useful for custom-built PCs or when you need to reinstall drivers after system formatting.
Check for BIOS Updates Motherboard manufacturers regularly release BIOS updates that can improve hardware compatibility and performance. Check your motherboard manufacturer’s website periodically for BIOS updates.
Monitor Driver Updates Set up Windows Update to automatically install driver updates, but review them periodically to ensure they’re working correctly. Some specialized hardware may require manual driver management.
Conclusion
Updating drivers in Windows 11 is a straightforward process when you know the available methods. Windows Update handles most driver updates automatically, but manual methods provide more control when needed.
Regular driver updates ensure optimal system performance, security, and hardware compatibility. Remember to create restore points before major driver installations and always download drivers from official sources to maintain system stability and security.



![How to Update Drivers in Windows 11 [Easy & Safe]](https://www.geeksdigit.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/extend-battery-life-windows-laptop.jpg)
![How to Update Drivers in Windows 11 [Easy & Safe]](https://www.geeksdigit.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/snipping-tool-shortcuts-windows-11.jpg)



