Experiencing a PC restart while gaming can be extremely frustrating. Whether you are immersed in a high-paced action game or playing a strategy title, an unexpected restart can ruin your gaming experience. Windows 11, though optimized for gaming with features like DirectStorage and Auto HDR, is not immune to this issue.
Multiple factors, ranging from hardware problems to software misconfigurations, can trigger random restarts. In this guide, we will explore all the possible causes of PC restarts during gaming on Windows 11 and provide detailed solutions to fix them.
Why Your PC Restarts While Gaming
Before diving into solutions, it is important to understand the reasons behind sudden restarts. Common causes include:
- Overheating – Gaming demands high CPU and GPU performance, which generates heat. If temperatures exceed safe limits, the PC may automatically restart to prevent hardware damage.
- Power Supply Issues – Insufficient or faulty power supply can cause restarts during gaming, especially with power-hungry components like high-end GPUs.
- Outdated Drivers – Graphics and chipset drivers that are outdated or incompatible with Windows 11 can lead to instability.
- Faulty RAM – Defective or unstable RAM modules may trigger system crashes or restarts during intensive tasks.
- Corrupted System Files – Damaged Windows system files can cause unexpected behavior during high-load processes.
- Overclocking Issues – Overclocked CPUs or GPUs might not be stable under heavy gaming workloads.
- Malware or Viruses – Malicious software can interfere with system performance, causing unexpected restarts.
- Software Conflicts – Background programs or poorly optimized game files may conflict with Windows processes, triggering a restart.
Understanding these causes helps narrow down the problem and apply the most effective solution.
Step 1: Monitor CPU and GPU Temperatures
Overheating is the leading cause of gaming-related PC restarts. When your CPU or GPU reaches critical temperatures, your system automatically shuts down to prevent permanent hardware damage. This protective mechanism is essential but indicates a serious cooling problem.
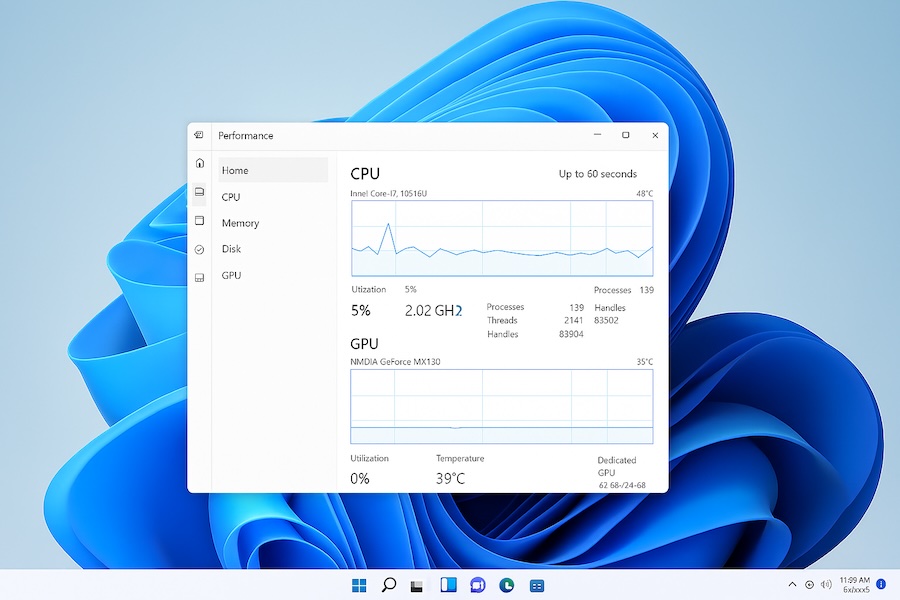
Start by monitoring your system temperatures using reliable software like HWMonitor, Core Temp, or MSI Afterburner. Run these programs while gaming and watch for temperature spikes. Your CPU should ideally stay below 80-85 degrees Celsius, while GPUs can handle slightly higher temperatures but should remain under 85-90 degrees Celsius during heavy gaming.
If temperatures are too high, several solutions can help. First, clean your PC thoroughly. Dust accumulation blocks airflow and reduces cooling efficiency dramatically. Use compressed air to clean all fans, heatsinks, and vents. Pay special attention to the CPU cooler and GPU fans, as these are critical components.
How to monitor temperatures:
- Use HWMonitor or Core Temp – These free tools display CPU and GPU temperatures in real-time.
- Check Windows Task Manager – Open Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc) → Performance tab → GPU/CPU sections.
- Use MSI Afterburner – Especially useful for gaming laptops and desktops to monitor GPU load and temperature.
Optimal temperatures:
- CPU: 40°C – 85°C (depends on model)
- GPU: 30°C – 85°C (depends on model)
How to fix overheating:
- Clean dust from fans and heatsinks.
- Reapply thermal paste on CPU/GPU if old or dry.
- Improve case airflow; add additional fans if necessary.
- Use a cooling pad for laptops.
- Lower graphics settings to reduce load on hardware.
Step 2: Check Power Supply Unit (PSU)
An inadequate or failing power supply unit is another major cause of gaming restarts. Gaming demands significant power, especially from modern high-end graphics cards. If your PSU cannot deliver sufficient wattage or has degraded over time, your system will restart when power demand peaks.

Calculate your system’s power requirements using online PSU calculators. Add your CPU, GPU, RAM, storage devices, and other components to determine the minimum wattage needed. Your PSU should provide at least 20-30 percent more power than your system’s maximum draw to ensure stable operation and account for efficiency losses.
Check your current PSU’s specifications. If it’s barely meeting your needs or is several years old, it might be failing. Power supplies degrade over time, and their capacitors lose the ability to deliver clean, stable power. Budget PSUs are particularly prone to early failure.
How to check your PSU:
- Ensure your PSU wattage meets your system requirements (use online PSU calculators).
- Listen for unusual fan noise or burning smells.
- Use a multimeter or PSU tester to check voltage stability.
Solution:
- Replace faulty or insufficient PSU with a quality unit from a trusted brand.
- Avoid cheap or low-efficiency PSUs, as they may not deliver stable power under load.
Step 3: Update Graphics and Chipset Drivers
Outdated or corrupted GPU drivers frequently cause gaming crashes and restarts. Graphics drivers are the software bridge between Windows 11 and your graphics card, and gaming performance heavily depends on having the latest drivers with bug fixes and optimizations.
For NVIDIA graphics cards, download drivers directly from the NVIDIA website or use GeForce Experience. Choose the latest Game Ready Driver for your specific GPU model. For AMD graphics cards, visit the AMD website and download the appropriate Radeon Software Adrenalin Edition drivers.
Steps to update drivers:
- Update GPU drivers:
- NVIDIA: Use GeForce Experience.
- AMD: Use Radeon Software.
- Update chipset drivers:
- Visit your motherboard manufacturer’s website.
- Download the latest chipset, audio, and network drivers.
- Update Windows 11:
- Settings → Windows Update → Check for updates.
Tip: Avoid beta drivers unless necessary, as they can be unstable.
Step 4: Run Windows Memory Diagnostic
Faulty or incompatible RAM can cause random restarts, especially under the memory-intensive conditions of modern gaming. RAM issues manifest in various ways, including crashes, restarts, blue screens, or corruption errors.
Run Windows Memory Diagnostic to check for RAM problems. Type memory diagnostic in the Windows search box and select Windows Memory Diagnostic. Choose restart now and check for problems. The tool will run several tests and report any issues found.
Steps:
- Press
Win + R, typemdsched.exe, and hit Enter. - Choose “Restart now and check for problems.”
- The system will reboot and scan your RAM for errors.
Solution: Replace defective RAM sticks if errors are detected.
Step 5: Scan for Malware
Malware can cause system instability and unexpected behavior including restarts during gaming. Malicious software consumes system resources and interferes with normal operations.

Consider using additional malware removal tools like Malwarebytes for deeper scanning. Some threats evade Windows Security detection. Run Malwarebytes in Safe Mode for the most thorough cleaning.
Check for potentially unwanted programs (PUPs) that might have been bundled with free software. Review your installed programs list and uninstall anything suspicious or unrecognized.
Steps to scan for malware:
- Use Windows Defender (built-in) → Full Scan.
- Use third-party scanners like Malwarebytes for a deep scan.
- Remove any threats and restart your PC.
Step 6: Check for Corrupted System Files
Corrupted Windows system files can cause various problems including unexpected restarts. Windows 11 includes built-in tools to scan for and repair damaged system files.
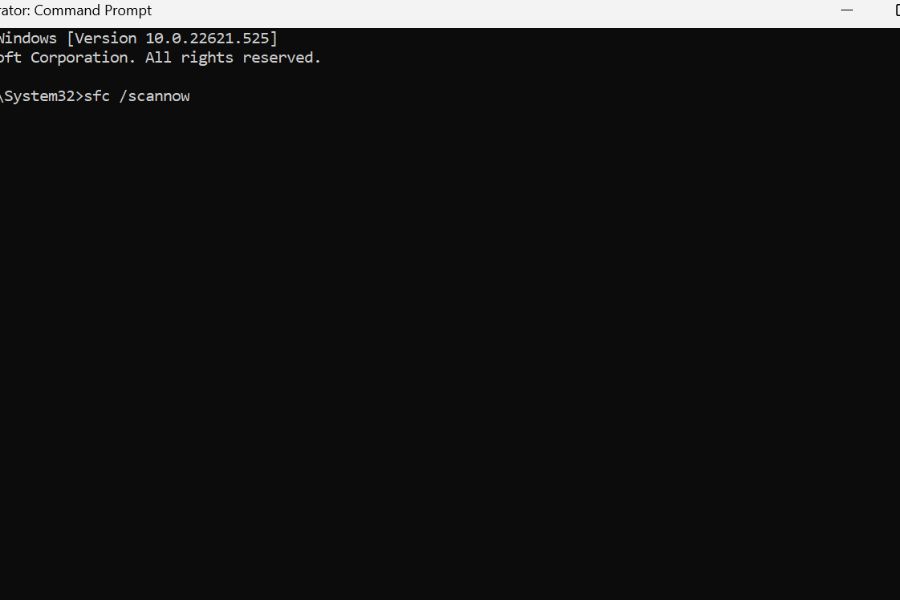
Open Command Prompt as administrator by searching for cmd, right-clicking it, and selecting Run as administrator. First, run the System File Checker by typing sfc /scannow and pressing Enter. This scan takes 15-30 minutes and automatically repairs corrupted files it finds.
Steps to repair system files:
- Open Command Prompt as administrator.
- Run
sfc /scannow– this scans and repairs corrupted Windows files. - If issues persist, run:
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth - Restart your PC after completion.
Step 7: Disable Automatic Restart
Windows 11 automatically restarts your PC when critical errors occur, which prevents you from seeing error messages that could help diagnose problems. Disabling this feature won’t fix the underlying issue, but it reveals valuable information.
With automatic restart disabled, you’ll see Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) error messages when crashes occur. Note the error codes displayed. These codes indicate specific problems like driver conflicts, hardware failures, or system file corruption. Research these error codes online for targeted solutions.
Steps:
- Press
Win + R, typesysdm.cpl, and hit Enter. - Go to Advanced → Startup and Recovery → Settings.
- Uncheck Automatically restart.
- Click OK and restart your PC.
Step 8: Check Event Viewer
Windows Event Viewer can help identify why your PC is restarting.
Steps:
- Press
Win + X→ Event Viewer. - Navigate to Windows Logs → System.
- Look for Critical errors marked with a red exclamation mark.
- Note the Event ID and error description; search online for specific fixes.
Step 9: Check Hard Drive or SSD Health
Faulty storage devices can cause games to crash or trigger restarts.
Steps:
- Open Command Prompt as administrator.
- Run
chkdsk /f /r C:and restart. - Use tools like CrystalDiskInfo to check SMART health status.
Solution: Replace failing drives to prevent data loss and restarts.
Step 10: Disable Overclocking
Overclocking can lead to instability, especially during gaming sessions that stress your CPU/GPU.
Steps:
- Enter BIOS/UEFI during boot (usually
DelorF2). - Reset CPU and GPU overclock settings to default.
- Save and exit BIOS.
Tip: Only overclock with proper cooling and stability testing using tools like Prime95 or FurMark.
Step 11: Adjust Windows 11 Power Settings
Windows 11 power settings can interfere with gaming stability. The default balanced power plan sometimes throttles performance to save energy, causing issues during demanding games.
Steps:
- Go to Settings → System → Power & Battery → Power Mode.
- Set to Best Performance or High Performance.
- Disable sleep or hibernation during gaming.
- In advanced settings, ensure Processor power management → Maximum processor state is 100%.
Step 12: Reinstall Problematic Games or Software
Sometimes a specific game or software may be corrupted, leading to restarts.
Steps:
- Uninstall the problematic game.
- Delete remaining game files in
DocumentsorAppData. - Reinstall the game from a trusted source.
Step 13: Update BIOS/UEFI
An outdated BIOS can cause instability with new hardware or Windows 11 features.
Steps:
- Check motherboard manufacturer’s website for the latest BIOS version.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to update BIOS.
- Reset BIOS settings to default after update.
Step 14: Check Network and Background Apps
Sometimes, online games may trigger instability if network drivers or background apps conflict.
Steps:
- Update network drivers.
- Close unnecessary background apps using Task Manager.
- Disable overlays (Discord, Steam, NVIDIA GeForce Experience) temporarily to test stability.
Step 15: Seek Professional Help
If none of the above steps work, the issue may be hardware-related:
- GPU defects or VRAM issues
- Motherboard problems
- Faulty PSU or power cables
Consult a certified technician to run a full diagnostic.
Conclusion
Random restarts while gaming in Windows 11 can result from multiple factors ranging from overheating and power issues to software conflicts and malware. By following the steps outlined in this guide—monitoring temperatures, checking hardware, updating drivers, scanning for malware, repairing system files, and adjusting power settings—you can significantly reduce or eliminate these unexpected restarts.
Consistent maintenance and monitoring of your PC’s health will ensure smooth, uninterrupted gaming sessions. Taking a proactive approach is key: regular driver updates, hardware checks, and maintaining a clean, optimized system will help you enjoy Windows 11 gaming to its fullest potential without interruptions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why does my PC restart only while gaming and not during normal use?
Gaming puts a heavy load on your CPU, GPU, and RAM. If your system overheats, your power supply cannot provide enough wattage, or drivers are unstable, Windows 11 may automatically restart to prevent hardware damage. Normal tasks like browsing or watching videos don’t stress your system enough to trigger these issues.
How can I check if overheating is causing restarts?
You can use monitoring tools such as HWMonitor, MSI Afterburner, or Core Temp to check your CPU and GPU temperatures. If temperatures approach the maximum safe limits (CPU ~85°C, GPU ~85°C), overheating is likely the cause. Improving airflow, cleaning dust, or lowering graphics settings can help prevent restarts.
Can a faulty power supply cause restarts during gaming?
Yes. A PSU that doesn’t provide sufficient or stable power can cause sudden restarts under heavy load. High-end GPUs and CPUs require stable power, especially during demanding games. If your PSU wattage is insufficient, replacing it with a high-quality unit from a reputable brand is recommended.
Will updating Windows 11 and drivers fix the problem?
Updating Windows 11 and all relevant drivers (GPU, chipset, audio, and network) often resolves compatibility and stability issues that can cause restarts. It ensures your system can handle modern games properly and fixes known bugs or conflicts with older drivers.








